ELECTRONIC WASTE RECYCLING
E Waste / Electronics Recycling:
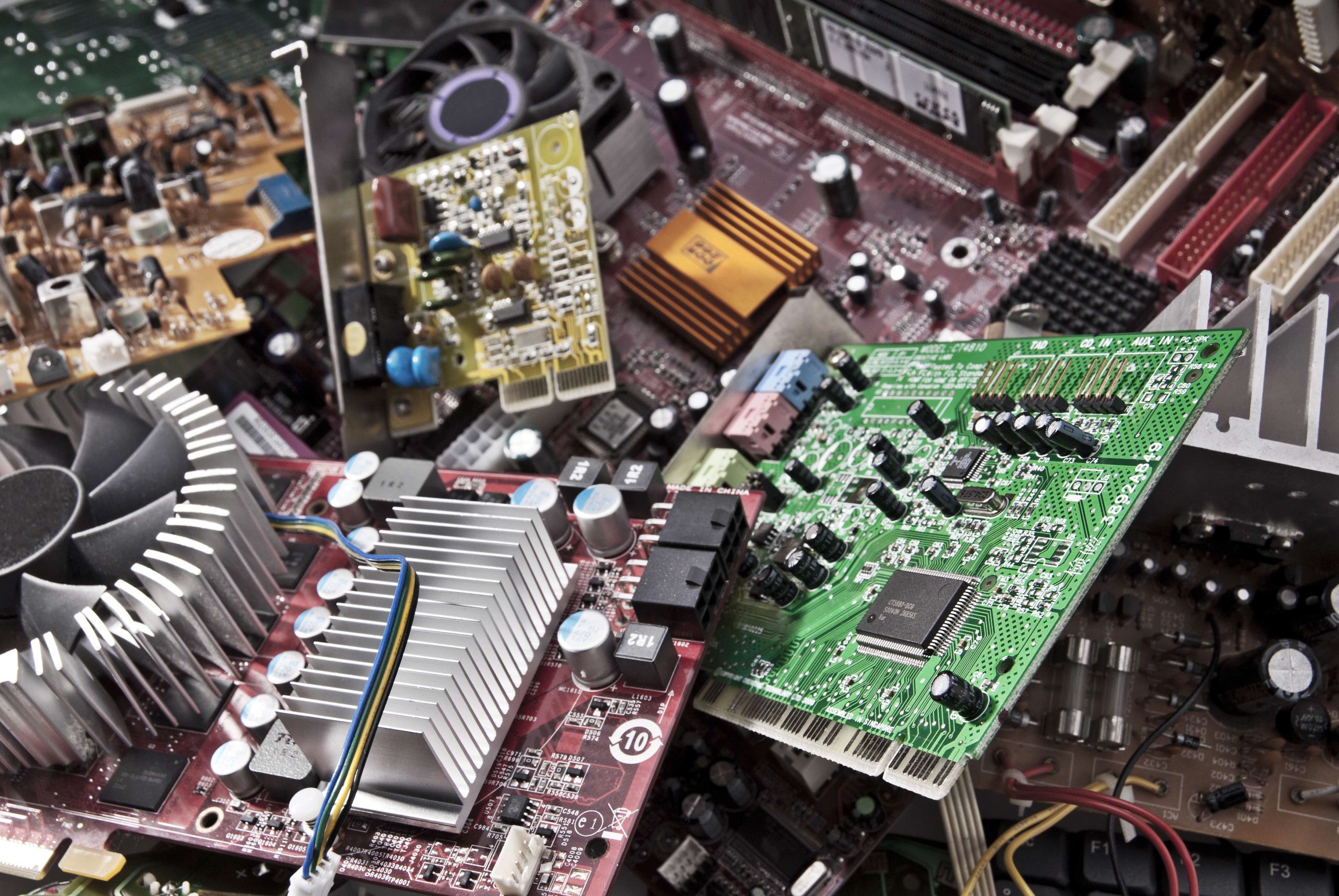
What to do with old computers and electronic waste
Electronic waste is usually described as the result of end-of-life electric and electronic equipment (EEE). E waste, or electronic waste, is the fastest growing solid waste stream in the world. Every year millions of electrical and electronic devices break or become obsolete and are thrown away. These discarded devices are considered e-waste and can become a threat to the environment and to human health if they are not treated, disposed of, and recycled appropriately. In 2019, an estimated 53.6 million metric tons of e-waste were produced globally, but only 17.4% was documented as formally collected and recycled. Global e-waste generation is estimated to reach 74.7 million metric tons by 2030, representing a significant environmental threat. E-Waste is increasing 3 times faster than the world’s population. E-waste streams contain valuable and finite resources that can be reused if they are recycled appropriately. Electronic waste recycling is essential to protect our environment. HazChem Environmental can pickup and recycle electronics for any commercial, industrial, manufacturing, educational or medical facility, providing environmental benefits and regulatory compliance.
Chicago Electronics Recycling
E-Waste encompasses a broad range of discarded electronic devices and equipment that have reached the end of their usable life. We specialize in industrial and commercial settings which includes various types of electronic equipment used for business operations, manufacturing processes, communication, and data storage. Some common examples of industrial or commercial e-waste recycling include:
- Computers and Servers: Desktop computers, laptops, servers, and data storage devices are frequently replaced in industrial or commercial settings due to technological advancements or the need for increased performance. This includes Batteries and CRT, LCD or LED Monitors.
- Office Equipment: Printers, copiers, fax machines, and scanners are essential office equipment that often become obsolete or malfunction over time, leading to their disposal as e-waste.
- Telecommunication Devices: Office phones, mobile phones, and networking equipment, such as routers and switches, contribute to e-waste when they are no longer in use or are upgraded to newer models.
- Industrial Machinery: Various types of industrial machinery, including manufacturing equipment, control systems, and instrumentation, may generate e-waste when they are decommissioned or replaced with more advanced technology.
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment: Electronic devices used in medical facilities, laboratories, and research institutions, such as diagnostic equipment, imaging machines, and analytical instruments, can also become e-waste when they reach the end of their lifespan.
It is Illegal in Illinois to Throw Some Electronic Devices into the Trash
To see a list of these items, please visit the electronics recycling page on the Illinois EPA website. Why is it illegal for these devices to go into a landfill? Electrical and electronic products contain hazardous materials. To protect our environment, these materials should not be entering into our land and water. Also, valuable metals may also be found in these devices such as copper, zinc, gold, silver, platinum, nickel and cobalt. These metals can be recycled and re-used in order to reduce waste and to promote sustainability and a circular economy.

Why is Recycling E-Waste So Important?
It is important to recycle e-waste for several reasons:
- Environmental Protection: Many electronic devices contain hazardous materials, including lead, mercury, cadmium, brominated flame retardants, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). Improper disposal of e-waste can lead to environmental pollution and pose risks to human health and ecosystems. Recycling e-waste helps prevent these harmful substances from entering the environment.
- Resource Conservation: Electronic devices contain valuable materials, such as precious metals (e.g., gold, silver, platinum) and rare earth elements (e.g., neodymium, lithium), which can be recovered and reused in the manufacturing of new products. Recycling e-waste conserves natural resources and reduces the need for raw material extraction.
- Energy Savings: Recycling e-waste requires less energy compared to the production of new electronic devices from raw materials. By recycling e-waste, energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with the manufacturing process are reduced, contributing to energy conservation and climate change mitigation.
- Data Security: Proper disposal of electronic devices is essential for protecting sensitive information and ensuring data security. Recycling e-waste through certified facilities helps prevent data breaches and identity theft by securely erasing or destroying data-containing components.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many jurisdictions have regulations and laws governing the disposal and recycling of e-waste to minimize its environmental impact and promote responsible waste management practices. Compliance with these regulations helps businesses avoid fines and legal penalties while demonstrating their commitment to environmental stewardship.
Overall, recycling e-waste in industrial or commercial applications is essential for minimizing environmental pollution, conserving resources, reducing energy consumption, safeguarding data security, and complying with regulatory requirements. By adopting responsible e-waste management practices, businesses can contribute to a sustainable and circular economy while protecting the planet for future generations.
Some of the Industries we serve are energy projects, government and municipalities, manufacturers, medical facilities, electronic car manufacturers, battery manufacturers, telecom companies, E-Commerce, IT services, education, chemical companies, equipment manufacturers, as well as any large office setting in any realm of business that generates e-waste or does upgrades on their systems.
The World Health Organization website provides more statistics on e waste and the associated facts and issues if you would like to learn more.
How Do You Dispose of E-Waste
Due to the number of internal hazardous components, e-waste is subject to the EPA’s RCRA laws. Most states implement the laws of the RCRA and create additional legislation that is at least as stringent as the federal laws. If you are hiring a waste management company to handle the entire e-waste disposal process, or if you are attempting to do it on your own, you must ensure that state laws, in addition to federal ones, are being adhered to. Your company’s generator status can influence the hazardous waste management process. For more information on your generator status, view the EPA’s categories of hazardous waste generators and consult the Code of Federal Regulations for exact regulations based on generator type.
The Electronic Recycling Process:
HazChem Environmental specializes in industrial, commercial and business e waste recycling. We do not do residential pickups.
Electronic waste (e-waste) undergoes a recycling process to recover valuable materials and components while minimizing environmental impact. Here’s an overview of what is typically done with e-waste for recycling:
Collection and Sorting: E-waste is collected from businesses and it is then sorted based on its type and condition to determine the most appropriate recycling methods.
Dismantling and Disassembly: E-waste is dismantled and disassembled into its constituent parts, such as circuit boards, cables, plastic casings, and metal components. This process may involve manual labor or automated machinery, depending on the scale and complexity of the e-waste.
Material Recovery: Valuable materials, such as precious metals (gold, silver, platinum), copper, aluminum, and rare earth elements, are recovered from e-waste through various recycling techniques. For example:
- Circuit boards are processed to extract precious metals and recover solder for reuse.
- Plastic components are shredded and melted down for recycling into new products.
- Metals are separated and smelted to obtain pure metal ingots for reuse in manufacturing.
Component Reuse and Refurbishment: Functional components and parts that are still in good condition may be reused or refurbished for resale or donation. For example:
- Working hard drives, memory modules, and optical drives from computers may be refurbished and sold as replacement parts.
- Functional displays, keyboards, and other peripherals may be reused in refurbished electronic devices.
Secure Data Destruction: Data-containing components, such as hard drives and memory chips, undergo secure data destruction to ensure that sensitive information is permanently erased. This may involve physical destruction (e.g., shredding) or data wiping techniques that overwrite data multiple times to prevent recovery.
Environmental Treatment: Hazardous materials, such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants, are carefully managed and treated to prevent environmental pollution. Specialized processes, such as neutralization, detoxification, and encapsulation, may be used to safely handle and dispose of hazardous substances.
Certification and Compliance: E-waste recycling facilities may undergo certification and compliance audits to ensure that they meet environmental standards and regulatory requirements. Certifications such as Responsible Recycling (R2) and e-Stewards demonstrate adherence to best practices in e-waste management and environmental stewardship.
End-of-Life Processing: After material recovery and component reuse/refurbishment, any remaining e-waste residues are processed for proper disposal or treatment. This may include landfilling, incineration (with energy recovery), or other environmentally sound disposal methods.
By following these steps, e-waste recycling facilities can effectively recover valuable resources, minimize environmental pollution, and contribute to a sustainable circular economy.
Our Team is always ready to deploy, 24 hours a day, 365 days per year, rain or shine, including holidays. We do not rely on automated answering systems for our main phone line (630) 458-1910. Instead, we guarantee that a live person will answer your call, regardless of whether it is a weekend, holiday, or any other day.
Combining Recycling Services with other industrial waste disposal is more efficient. Learn about our other Industrial Recycling, Cardboard Recycling, Commercial Plastic Recycling and View other HazChem Services.

Compliant. Responsive. Safe.
Call 630-458-1910 for immediate assistance. Open 24/7/365
For a FREE, no-obligation quote, click the button below

